What is the current state of Japan's maternal mortality rate?
The maternal mortality rate is a number that measures the percentage of women who die during pregnancy or childbirth. I will explain the current state of Japan's maternal mortality rate from a global perspective, along with specific figures. Let's learn why pregnant women die, the specific reasons and countermeasures.
ELEMINIST Editor
Eleminist Editorial Department
We will deliver the latest sustainable information carefully selected from Japan and around the world from the unique perspective of an eleminist. A guide to ethical and minimal living and consumption, and a sustainable way of life.
2021.11.30What is maternal mortality? Definition and method of calculation
A measure of the proportion of pregnant women who died from "all causes" related to or aggravated by pregnancy or its management, but not related to pregnancy. The formula for calculating the maternal mortality rate is as follows. Maternal mortality rate = (yearly number of maternal deaths / annual number of births) x 100,000 The number of births per year is calculated by "number of births + number of stillbirths" or "number of births per year." However, the annual number of maternal deaths does not include the number of deaths due to unintentional or accidental causes. The survey is conducted annually with the aim of examining the environment surrounding pregnant women and children in specific countries, regions, and the world at large. (*1)
Present Status of Maternal Mortality in Japan
According to the 2019 State of the World's Children Report published by UNICEF, there were 44 maternal deaths in Japan in 2017. The maternal mortality rate was "5". The number of pregnant women who died was calculated to be 1 out of 16,700, which can be said to be the lowest level in the world. (*2) However, the maternal mortality rate was not always low in Japan. According to data released by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, the maternal mortality rate in the early 1900s was around 400 per 100,000 live births. Since then, the mortality rate has decreased significantly with the development of medical technology. The maternal mortality rate in the 1980s was around 15. It can be said that it has been close to the current level since the late 1990s. (*3) Countries with maternal mortality rates equivalent to Japan as of 2017 include Denmark, Ireland, and Switzerland. However, the fact remains that it is not uncommon for countries with maternal mortality rates to exceed 500. (*4)
What is the status of the maternal mortality rate in the world?
From here, let's focus on the maternal mortality rate in the world. What are the characteristics of countries with high and low maternal mortality rates?
| Country Name | Maternal Mortality |
| South Sudan | 1,150 |
| Chad | 1,140 |
| Sierra Leone | 1,120 |
| Nigeria | 917 |
| Somalia | 829 |
| Mauritania | 766 |
| Guinea Bissau | 667 |
| Liberia | 661 |
| Afghanistan | 638 |
| Ivory Coast | 617 |
| Gambia | 597 |
| Guinea | 576 |
| Mali | 562 |
| Burundi | 548 |
| Lesotho | 544 |
| Cameroon | 529 |
| Tanzania | 524 |
| Niger | 509 |
| 480 | |
| Haiti | 480 |
| Democratic Congo Republic | 473 |
| Country | Maternal Mortality th> |
|---|---|
| Belarus | 2 |
| Italy | 2 |
| Norway | 2 |
| Poland | 2 |
| Czech | 3 |
| Finland | 3 |
| Greece | 3 |
| Israel | 3 |
| United Arab Emirates | 3 |
| Denmark | 4 |
| Iceland | 4 |
| Spain | 4 |
| Sweden | 4 |
| Austria | 5 |
| Belgium | 5 |
| Ireland | 5 |
| Japan | 5 |
| Luxembourg | 5 |
| Netherlands | 5 |
| Slovakia | 5 |
| Switzerland | 5 |
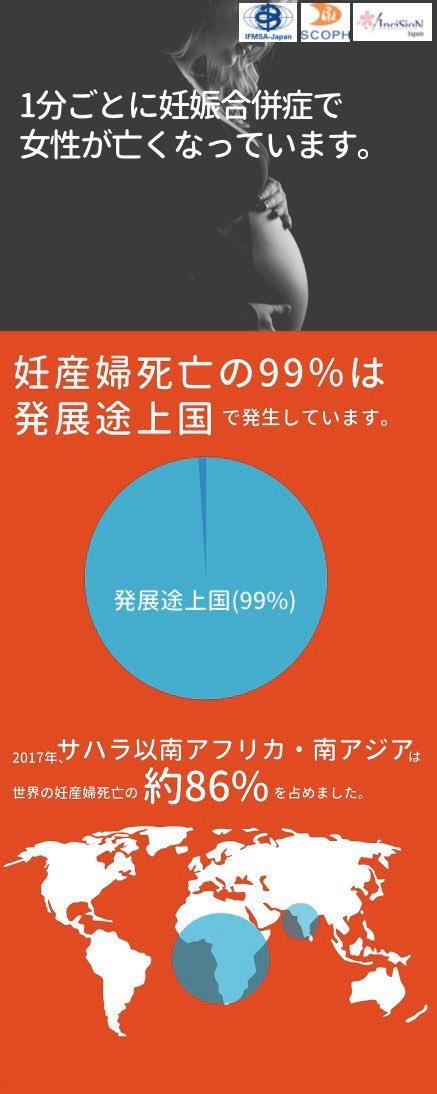
By region, you can see that there are many in Europe, especially in Western Europe. Many countries with low maternal mortality rates are economically developed and politically stable. Medical care is also well developed, and it can be said that a major feature is that all citizens can receive necessary medical care in situations where they need it. (*5) Countries with high maternal mortality rates are often found in so-called developing countries. According to WHO, 94% of maternal deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries. In addition to the fact that medical care is not developed, the high mortality rate is probably related to the fact that there are many high-risk pregnant women, such as pregnancy and childbirth at a young age. (*6)
The reasons for maternal mortality and required countermeasures
Now that I know the current state of the maternal mortality rate in the world, I am curious about the reasons. According to the "Maternal Death Reporting Project 2019" announced by the Japan Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the main reasons and percentages of maternal deaths in Japan are as follows. (*7) Obstetric critical hemorrhage 19% Cerebral hemorrhage 14% Cardiopulmonary collapse-type amniotic fluid embolism 11% Cardiovascular disease 9% Infection 9% Detailed reasons for each of the top three rankings are explained below.
It is a case of death due to excessive bleeding associated with pregnancy and childbirth. Uterine-type amniotic fluid embolism and uterine rupture are common causes of worrisome bleeding. It continues to be the most common cause of maternal death in Japan. In 2010, about 30% of maternal deaths were caused by critical obstetric bleeding. In recent years, it has fallen to around 20%. (*8)・Measures Measures to prevent deaths are all about early detection and early treatment. If you experience any symptoms that make you feel unwell, you should seek immediate medical attention. It is also important to improve the environment and develop human resources so that appropriate measures can be taken immediately in the medical field.
During pregnancy, blood flow increases to nourish the fetus, which can cause vascular problems. It often occurs in the second to third trimester of pregnancy. It is known that many pregnant women who develop cerebral hemorrhage have been diagnosed with pregnancy-induced hypertension. The percentage of maternal death causes is about 13 to 15% every year. No significant decrease. (*9)・Countermeasures Along with obstetric critical bleeding, early detection and early treatment are key to saving lives. Also, from the early stages of pregnancy, it may be necessary to adjust your eating habits and lifestyle so that you do not develop pregnancy hypertension syndrome. It is also important for expectant mothers themselves to be aware of the risks.
Amniotic fluid embolism occurs when fetal components in the amniotic fluid flow into the mother's body. Many cases of cardiopulmonary collapse and even death have been reported. Dyspnea, chest pain, and shock symptoms occurred. Many cases occur during pregnancy and childbirth, and pregnant women over the age of 35 are said to be at high risk. (*10) Concerns about countermeasures Initial symptoms of collapsed amniotic fluid embolism are diverse. If you experience chest pain, difficulty breathing, unexplained drop in blood pressure, or loss of consciousness, seek medical attention immediately. Once the disease develops, there have been many reports of life-threatening cases in a short period of time, so it is important not only for medical personnel but also for expectant and nursing mothers themselves to be aware of the risks. Caesarean section is especially risky for those who are 35 years old or older at the time of delivery, so it is necessary to create a system that can respond immediately in the event of an emergency.
Let's learn from maternal mortality rates in Japan and around the world
Pregnancy and childbirth are not illnesses. However, in reality, there have been reports of cases in which pregnancy or childbirth causes illness or other troubles that lead to death. Japan's maternal mortality rate is extremely low even by global standards. It can be said that it is one of the countries where women can have children with peace of mind. However, looking around the world, there are still many countries and regions with extremely high maternal mortality rates. While looking at the reasons why pregnant women die, let's learn about the measures that will be needed in the future.
*1 Explanation of main ratios and terms used in health statistics | Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare *2 Maternal and newborn health index Maternal and newborn health index | Next trends (pages 1-2) | Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare *4 Maternal and newborn health index Maternal and newborn health index | unicef *5 Maternal and newborn health index Maternal and newborn health index | unicef
*6 Maternal Mortality | WHO Association of Japan*7 Maternal Death Reporting Project 2019 (page 4) | Japan Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists 9 Characteristics of Stroke in Pregnancy|Nippon Iji Shinposha Stroke in Pregnant Women|Ikeda Neurosurgery Maternal Death Reporting Project 2019 (page 5)|Japan Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists*10 Amniotic fluid embolism|Japan Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Neonatal Hematology Society
*The information posted is as of November 30, 2021.

!["Rucksacks and backpacks" best-selling ranking Coleman and North Face are popular [June 2021 edition]](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_9/2022/3/29/a9647069022c61ee44fb85806ae07d8b_0.jpeg)