ASCII.jp What happens if you make a mistake in the default gateway settings?
The default gateway is a router that is the exit to a different network.Therefore, if you do not set the default gateway address, you will not be able to interact with other networks.What is happening at this time?
What is the role of the default gateway?
The default gateway is a type of router used for "routing" (route control).Routing is the control of how the packet is transmitted from the source computer to the destination computer.
There are two routing methods: "direct routing", which sends packets to the computer of the destination directly, and "indirect routing", which asks a router to relay packets.
How to send a packet to a computer is determined using the "routing table" (route control table) in the computer.The routing table is registered with which LAN card (network interface) and which routers should be sent from which router to send packets.
Each network interface can be connected to a different subnet.And each subnet has a router as a relay point, and is further connected to the outer network.This relay is "Gateway".At the end of the gateway, there are other networks and computers.In other words, the routing table has a network and computer, which is the end destination of the packet, as well as the exit when sending a packet from the computer, the broadcast point for going to the outer network from the exit, and the final destination of the packet.
Direct routing is used to send packets to computers in the subnet.In the routing table, the range of the subnet is automatically registered for each network interface.If the computer is in the same subnet, data can be transmitted only with Ethernet and ARP mechanisms without a router.
If you can't send it directly by routing, use an indirect routing to have a router relay the packet.In the case of indirect routing, the route to the destination computer is selected from three types: "Host route", "Network Cruet", and "Default route" registered in the routing table (Fig. 1).
Figure 1 There are various methods for routing (route control)
Host route is the route to a specific destination computer.For example, the wired Ethernet port should be in -house LAN and Airh has a laptop that is connected to the provider's network at the same time. In the case of Windows, the dial -up connection that users can connect arbitrarily has a higher priority.You may try to access the in -house LAN server via Airh.
However, the provider's network should not be connected to the internal LAN, so it is not possible to use the internal LAN server.Therefore, the server of the in -house LAN is specified with an IP address and a subnet mask, and the route and network interface, which are the routes, are registered in the routing table.The route to this specific host is the host route.Also, if you specify the entire company LAN with an IP address and a subnet mask instead of a specific host, you can specify a route to a specific network.This is the network crute.
On the other hand, a default route refers to a "other" route, not direct routing, hostet, nor network crew.When a packet is sent to a computer, the TCP/IP function of the OS tries to select the route in the routing table.At this time, the default route is used when the routing table does not find the right route.
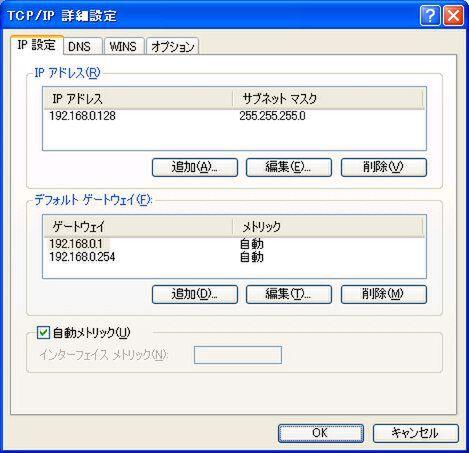
Run "Route Print" at the command prompt to display a computer routing table.Of the several items, "Network Destination" and "Net Mask" are "0.0.0."0" is the default route.It also shows that the router set as the default gateway is registered in the routing table as an IP address in the default route "Gateway".A default gateway means a gateway for the default route.
(Next page, following "Make a mistake in the default gateway")


![[Osaka Marriott Miyako Hotel] Plenty of cheese! Italian buffet held company release | Nikkan Kogyo Shimbun electronic version](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_9/2022/3/28/1061eb31530c979d7b766ae1877b113a_0.jpeg)




